Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are bacterial infections in the urinary system. Most of the time, UTIs are caused by bacteria, however, in some cases it can be due to fungi and in extreme cases by viruses. UTIs are the most common infections in humans and usually not serious, though there can be exceptions.
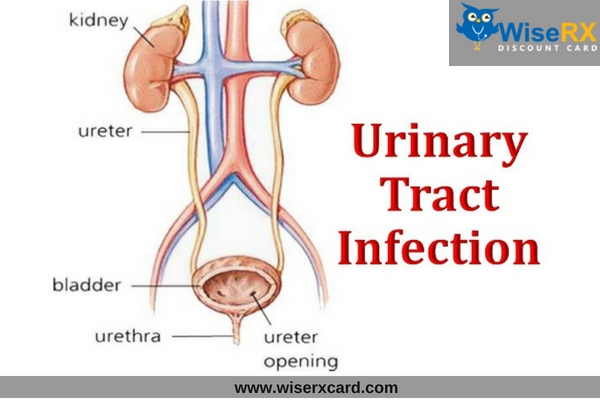
Urinary Tract Infection can happen anywhere in the urinary tract. The urinary tracts consists of kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. If UTI is in kidney, doctors call it pyelonephritis and if it’s in bladder then it is cystitis.
Who Gets Urinary Tract Infections?
Any person can get infected due to urinary tract, however, the chances of infection are more, if that person:
- Is a woman
- Has been through menopause
- Has had UTIs before
- Uses spermicide or diaphragm for birth control
- Is overweight
- Has a condition, such as spinal cord injuries, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease etc.
- Is a man who has sex with men, has HIV, or hasn’t been circumcised
- Has something that blocks the passage of urine, such as a tumor, kidney stone, or an enlarged prostate
Symptoms Of Urinary Tract Infections
Symptoms of a UTI vary from part to part i.e., depends on the part infected due to urinary tract. Lower tract UTIs affect the urethra and bladder. Few symptoms of a lower tract UTI are:
- increased urgency of urination
- burning with urination
- increased frequency of urination without passing much urine
- bloody urine
- cloudy urine
- urine that looks like cola or tea
- urine that has a strong odor
- pelvic pain in women
- rectal pain in men
Upper tract UTIs affect the kidneys. The risk of life-threatening diseases increase if bacteria transfers into the blood through infected kidney. Symptoms of an upper tract UTI include:
- chills
- fever
- nausea
- vomiting
- tenderness and pain in the upper back and sides
Causes Of Urinary Tract Infections
In most of the cases, UTI is due to bacteria (such as E. coli.) and is normally found in gut. Other bacteria that can cause UTI in the gut are Staphylococcus, Klebsiella, Proteus, Enterococcus, and Pseudomonas.
Sometimes, UTI can be found in bladder of both, men and women. It can occur due to sexually transmitted infections during unprotected sex. Some of the bacteria that can lead to bladder UTI are Chlamydia trachomatis, mycoplasma, and ureaplasma. The parasite trichomonas can also cause similar symptoms.
You’re more prone to get UTI if your immune system is weak due to an autoimmune disease or diabetes. This happens because your body doesn’t have much strength to fight off the germs that cause these infections.
Treatment For Urinary Tract Infections
Treatment of UTIs depends on the cause. Your doctor may recommend you some tests to diagnose which organism is causing the infection. In most cases, the cause of UTI is bacteria and is treated with antibiotics.
However, if UTI is due to viruses or fungi, it can be treated with antiviral drugs. Most of the doctors’ prefer ‘the antiviral cidofovir’ drug to treat viral UTIs. Fungal UTIs are treated with medications called antifungals.
Prevention Of Urinary Tract Infections
An individual can prevent UTI by following these tips:
- Make sure to drink at least 6-8 glasses of water daily.
- Avoid holding urine for long periods of time.
- If you experience urinary incontinence or difficulty in completely emptying your bladder, consult with your doctor immediately.
- For postmenopausal women, using topical estrogen prescribed by your doctor could make a difference in preventing UTIs.
- If you get UTI due to sexual intercourse, your doctor may recommend to take preventive antibiotics after intercourse, or long-term. Some studies have shown that long-term preventive use of antibiotics in older adults reduced the risk of UTIs.
- You can also take cranberry supplements or use vaginal probiotics (lactobacillus) to prevent UTI. Some studies suggest that regular use of probiotic vaginal supplements reduce the chances of occurrence and recurrence of UTIs, by changing the bacteria found in the vagina.
Just make sure to discuss it with your doctor to find the right prevention plan for you.